CABLE GLANDS:
A device designed to permit the entry of cable in to electrical equipment which provide sealing , retention and earthing, bonding, insulation, strain relief or combination of all these. Gland should maintain overall integrity of enclosure in to which it is to be fitted.
TYPE OF GLANDS:
- Brass Indoor Type Gland
- Brass Outdoor Type Gland
- Brass Straitening Unarmoured Cable Gland
- Brass Weather Proof Gland
- PG Threaded Gland
- Industrial Type Gland
HOW DO YOU KNOW WHICH CABLE GLAND IS SUITABLE FOR YOUR USE?
There are numerous options available, but there is no one–size–fits–all solution. However, it does imply that you can select a cable gland based on your specifications. To accomplish so, you must first take into account a variety of
environmental and application factors.
THE ENVIRONMENT’S PART:
It makes no difference if you work in aerospace, industrial, maritime, power & utility, telecommunications, or any other critical business. What matters is that you figure out what your cable gland’s primary application environment is.
Questions to ponder:
- Will you be utilising it indoor or outdoor?
- Will it be in a safe industrial zone or in a potentially dangerous or
explosive environment? - What is the current temperature, and is it stable?
- Is the environment humid or dusty?
- Are there any corrosive materials or gases nearby?
Your responses will assist define the cable gland specifications and whether a special protective planting or coating is required.
KNOWING THE TYPE OF CABLE:
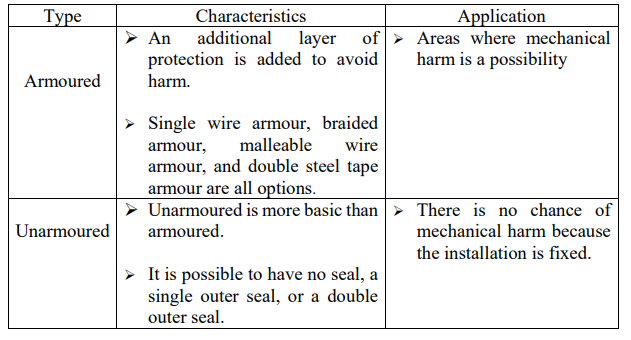
Different cables necessitate different cable glands. Understanding how to install an armoured cable gland, for example, differs from installing unarmoured cable glands.
CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING FACTORS WHEN DETERMINING THE RIGHT CABLE GLAND SIZE FOR BOTH TYPES:
- Diameter of the cable.
- Dimensions of the construction.
FOR ARMOURED CABLE, YOU MUST ALSO CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING:
- The inner bedding’s diameter.
- The lead covering’s diameter.
- The cable armour’s short circuit fault rating.
- The armour braid’s kind and size.
MATERIAL TYPES FOR CABLE GLANDS:
Depending on the application, environment, and cable type, different cable gland materials behave differently.
- Metal cable glands are utilised in a variety of applications, including the chemical industry, technology, and sectors where strong mechanical and chemical stability is required. The advantages are its long-term durability and stiff stability, even in damp situations.
- Due to its claw and seal construction, plastic cable glands have a wide cable range, making them particularly versatile to a variety of applications. Resistance to salt water, oil, and mild acids are just a few of the benefits.
MOUNTING DIFFERENT TYPES:
There are a variety of cable gland mounting options available depending on your application requirements, including:
- Compound or adhesive
- Bolted or flanged
- nut or threaded
- Installed, welded, and cast
CHECKLIST FOR FINAL SELECTION:
There are a few significant considerations that don’t fit into any of the aforementioned categories. So, before you choose a cable gland, consider the following questions:
Is the wire hole diameter large enough to accommodate all of the system’s cables?
- Is the cable’s diameter adequate?
- Is the pressure rating sufficient for your application’s requirements?
- Is the diameter of the mounting hold large enough for my cable
gland? - Is the gland thread metric or PG in depth and size?
- Is it necessary to use stopper plugs to seal up any unneeded cable
entries?
References:
1. EN50262 –European Standard.
2. CMP product – Cable Gland.




No comment