Insulation Coordination:
Voltage stresses in power systems can have internal or external origin. Overvoltages can be caused by faults, switching operations or lightning strokes. In addition, they can occur with very wide range of waveshapes and durations. Dielectric failures in power systems can cause tripping of the protective devices, destruction of equipment, or interruption of operation. The breakdown characteristics of the different types of insulation depend on the configuration and environment of the insulation, as well as on the waveshape and duration of the applied voltage. On the other hand, both stresses and withstand insulation voltages may exhibit a random behavior. Therefore, it is important not only to assess the overvoltages that can appear on a given component but the behavior of its insulation taking into account that stress and withstand characteristics may be random.
Insulation coordination is defined as the selection of the dielectric strength of equipment in relation to the voltages which can appear on the system for which the equipment is intended and taking into account the service environment and the characteristics of the available protective devices. In an insulation coordination study, the voltage levels of power system equipment are determined in order to ensure the protection of equipment against overvoltages. This proper design in terms of the insulation coordination provides the reliability of the system by decreasing insulation failures and reduces the cost of the system by preventing oversizing of the equipment. Hence, insulation coordination is an important study for power systems in order to prevent failures and overinvestment.
Power systems are always subjected to overvoltages, which are usually the result of faults, sudden changes in operating conditions caused by switching operations, or the impact of lightning strokes. Therefore, the over voltages can occur due to external agent such as lightning or due to internal agents such as switching operations, load rejection, internal faults. Etc.,
Purpose of Insulation Coordination:
To ensure that the probability of insulation breakdown is limited to an acceptable value and that any breakdown is restricted to self-restoring insulation.
System Transients in Power Systems:

Overvoltages in Power System:
Classification of Overvoltages:
An overvoltage is a voltage, between one phase and earth or between two phases, having a crest value exceeding the corresponding crest of the maximum system voltage.
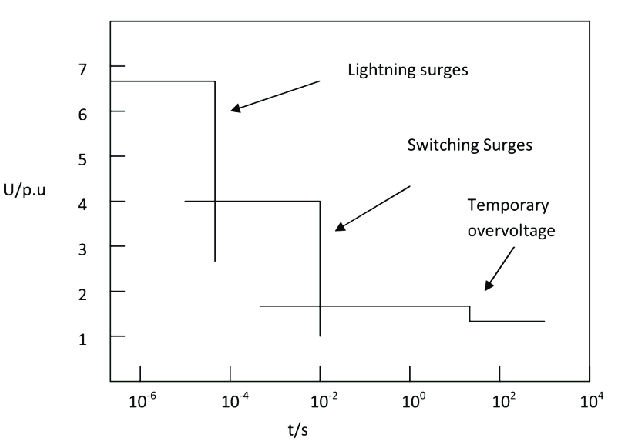
Standards classify the different types of overvoltages, according to classes and shapes, into four groups (IEC 60071-1, 2010; IEC 60071-2, 1996; IEEE Std C62.82.1, 2010; IEEE Std 1313.2, 1999):
Classification of Overvoltage:
- Temporary Over voltage (TOV)
- Slow front Overvoltage (SFO)
- Fast Front Overvoltage (FFO)
- Very fast front Overvoltage (VFFO)
Classes and Shapes of Over Voltages as per IEC 60071-1

Conclusion:
In this article, it is discussed about the summary of the insulation coordination and the insulation coordination has to be done to the selection of the dielectric strength of equipment in relation to the voltages which can appear on the system for which the equipment is intended and taking into account the service environment and the characteristics of the available protective devices. The power system may affect from the different types of over voltages such as TOV, SFO, FFO, VFFO. Most of the over voltages occurred in a power system is mainly due to switching operation such as transformer energization, line energization, capacitor bank switching etc., In order to protect the system from these over voltages, we need to coordinate the insulation of the HV equipment by doing insulation coordination studies.
Reference:
1. IEC 60071 – 1 : Insulation Coordination – Part 1: Definitions, principles and rules.
2. Jose L. Naredo et. al., Introduction to Transient Analysis of Power System
VIDHYA SAGAR DEVENDRAN
– Power System Engineer



No comment