Types of zip load
Power system loads are classified by one or a combination of the following types (To account for the voltage dependence).
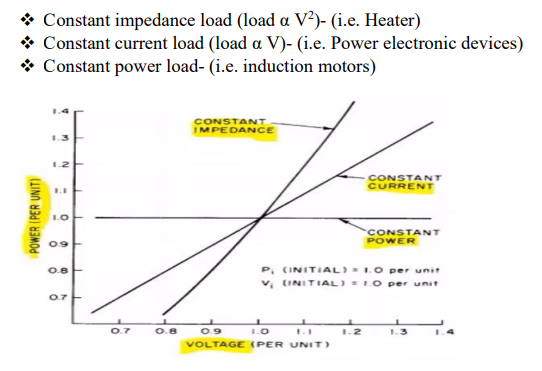
Waveform of different types of ZIP load
General equation used in the ZIP load,

Where,
S-Power at voltage V, Si- Initial power at voltage Vi, when
k=0 (for constant power load; k=1(for constant current load); k=2(for constant
impedance load.
Expanding the above equation,
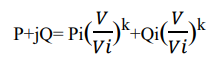
In case of ZIP Load
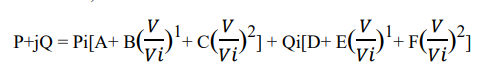
Where,
A&D-constant power load factor; B&E- constant current load factor; C&Fconstant impedance load factor.
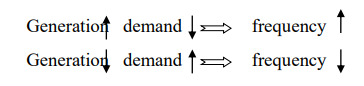
In case of frequency deviation the apparent power of ZIP load can be calculated base on below formula,
![]()
Where, G&H are the fraction of Pi&Qi respectively, when being affected by the frequency deviation. The below cases are represents the frequency deviation of the system.
Q1: 10MW constant impedance load, voltage source=0.90p.u. Real power=?
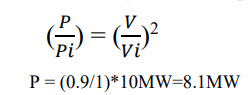
The source voltage is reduced to 0.9 p.u, so the 10MW load consumes only 8.1MW power (assume pf is unity). From the results of simulation the sending end voltage is equal to receiving end voltage (Because reactive power absorption or delivering is zero).
Q2: 25MW constant current load and source voltage 0.95p.u. Real power=?
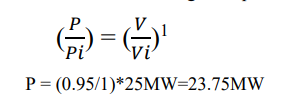
The source voltage is reduced to 0.95 p.u, so the 25MW load consumes only 23.75MW power (assume pf is unity). From the results of simulation the sending end voltage is equal to receiving end voltage (Because reactive power
absorption or delivering is zero).
Q3: 100MW polynomial load consist of 30% constant power, 25% constant impedance and 45% of constant current load. Supplied voltage 1.03pu, Real power=?
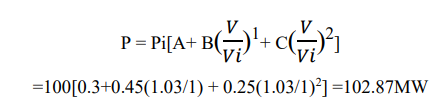
The source voltage is increased to 1.03 p.u, so the 100MW load consumes 102.87 MW power (assume pf is unity). From the results of simulation the sending end voltage is equal to receiving end voltage (Because reactive power
absorption or delivering is zero)
Simulation results of ZIP load
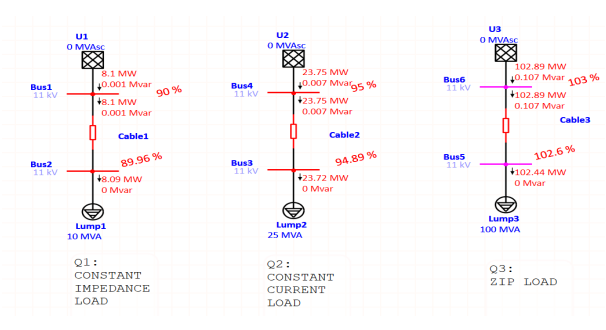



Zip load
Please how can I simulate a ZIP load on simulink with a boost converter for system stability purpose.