What is Insulation Coordination?
As per IEC 60071-1:2019 Part 1, the insulation coordination is “Insulation coordination comprises the selection of the electric strength of equipment and its application, in relation to the voltages which can appear on the system for which the equipment is intended and taking into account the characteristics of available protective devices, so as to reduce to an economically and operationally acceptable level the probability that the resulting voltage stresses imposed on the equipment will cause damage to equipment insulation or affect continuity of service”
In other words, Insulation coordination is the selection of the minimum insulation strength (or minimum clearance, since minimum insulation strength reduce the economic burden) required to withstand the expected temporary and transient overvoltage reach to the equipment.
Standards for Insulation Coordination
The following International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) are used commonly along with the Conseil International des Grands Réseaux Electriques (CIGRE) recommendations. In India, the IEC standards (given below) was adopted by the Bureau of Indian Standards (IS) on the recommendation of the High-Voltage Engineering Sectional Committee and approval of the Electrotechnical Division Council.
- IS/IEC 60071-1:2019 Part 1: Definitions, principles and rules.
- IS/IEC 60071-2:2023 Part 2: Application guidelines.
- IS/IEC TR 60071-4:2004 Part 4: Computational guide to insulation co-ordination and modelling of electrical networks.
- IEC 60071-11:2022 Part 11:Definitions, principles and rules for HVDC system
- IEC 60071-12:2022 Part 12: Application guidelines for LCC HVDC converter stations
- 82.1-2010 – IEEE Standard for Insulation Coordination–Definitions, Principles, and Rules
- 82.2-2022 – IEEE Guide for the Application of Insulation Coordination
Significance of Insulation Coordination
Insulation coordination will be used to design an optimal insulation level and required protection devices to ensure the safe operation of the system during adverse voltage conditions. Currently, Insulation coordination is become a mandatory requirement to the electrical system in order to demonstrate the compliance against the IEC / IEEE standards and the respective Electricity Transmission Codes. The design parameters in the IEC / IEEE standards shall be followed subject to fulfil the design paraments mentioned, however due to the geographical condition, it is advisable to do the Insulation coordination to have an accurate design parameter that suits to the respective network/ plant.
Economics behind the Insulation Coordination
Inadequate selection of insulation and protective devices can cause significantly higher voltages which may leads damage to equipment, property and personals. For example, loosing a transformer due to inadequate insulation design may lead loss of energy supply to the customer, which leads to revenue losses, regulatory obligations and reputational risk to the organisation.
Types of Insulation:
External Insulation
External insulation is the distances in open air or across the surfaces of solid insulation in contact with open air that are subjected to dielectric stress and to the effects of the atmosphere. Examples of external insulation are the porcelain shell of a bushing, bus support insulators, and disconnecting switches.
Internal Insulation
Internal insulation is the internal solid, liquid, or gaseous parts of the insulation of equipment that are protected by the equipment enclosures from the effects of the atmosphere. Examples are transformer insulation and the internal insulation of bushings. Equipment may be a combination of internal and external insulation. Examples are a bushing and a circuit breaker.
self-recovering insulation
Insulation which will recover its insulating properties after a disruptive discharge (flashover) caused by the application of a voltage is called self-restoring insulation. This type of insulation is generally external insulation, such as Air-insulation.
non-self-recovering insulation
Insulation that loses its insulating properties or does not recover completely after a disruptive discharge caused by the application of a voltage is called non-self-restoring insulation. This type of insulation is generally internal insulation, such as solid dielectrics, oil paper, oils or gases.
Different types of insulation coordination study?
Several studies can be performed under the insulation coordination using the software tools depends upon the different types of overvoltages mentioned in the above standards:
- Temporary overvoltages (TOV): They are undamped or weakly damped oscillatory overvoltages measured between phase to-earth or phase-to-phase for long duration. Temporary overvoltages occur due to phase to earth faults, generator overspeed, load rejection, resonance and ferro-resonance due to inductive and capacitive elements, or by a combination of all the above.
- Slow-front overvoltages (SFO): They are unidirectional or oscillatory overvoltages, with a slow front, highly damped for short-duration (microseconds to milli seconds). These overvoltages are caused by switching overhead line, cables, indictive and capacitive equipments, during the initiation and clearance of faults, or lightning strikes at the remote end of the overhead line / stations.
- Fast front overvoltages (FFO): They are transient overvoltages whose fast front shape for short duration (microseconds) is caused by switching operation at the nearest location or lightning strikes or even during the initiation of the fault. The lightning effect can be (a). a direct stroke on a phase conductor; (b) a direct stroke to earth wire or a tower top when lightning hits a shielded line; (c) an induced voltage when the lightning strike occurs to earth in the vicinity of the line.
- Very fast-front overvoltages (VFFO): They are the result of switching operations at the high voltage GIS equipment or faults.
Table -1 of IS/IEC 60071-1:2019 Part 1: Definitions, principles and rules, provides the Classes and shapes of overvoltages, Standard voltage shapes and Standard withstand voltage tests, the same shall be referred in the below link as well.
https://powerprojectsindia.com/classification-of-over-voltage-insulation-coordination-study/
voltage and time between different voltage surges are given below
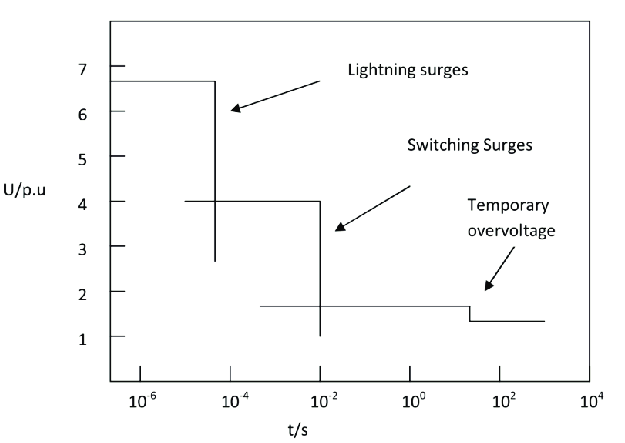
Correspondence between events and most critical types of overvoltages generated given in IS/IEC TR 60071-4:2004 s given below
| Temporary Overvoltages (TOV) | Transient Overvoltages | |||
| Slow Front Overvoltage (SFO) | Fast front overvoltages (FFO) | Very fast-front overvoltages (VFFO) | ||
| Load rejection | × | |||
| Transformer Energization | × | × | ||
| Parallel line resonance | × | |||
| Uneven breaker poles | × | |||
| Back feeding | × | |||
| Line fault application | × | × | ||
| Fault clearing | × | × | ||
| Line energization | × | × | ||
| Line re-energization | × | × | ||
| Line dropping | × | × | ||
| AIS busbar switching | × | 1) | ||
| Switching of inductive and
capacitive current |
× | × | × | |
| Back flashover | × | |||
| Direct lightning stroke | × | |||
| Switching inside GIS substation | × | |||
| SF6 circuit-breaker inductive and
capacitive current switching |
× | × | × | 1) |
| Flashover in GIS substation | × | |||
| Vacuum circuit-breaker switching | × | × | ||
| 1) In the case of short distance busbars and low damping, very-fast-front overvoltages can also occur. | ||||
Correspondence between events and most critical types of overvoltages generated given in IS/IEC TR 60071-4:2004 s given below
Selection of protective equipment against the over voltage:
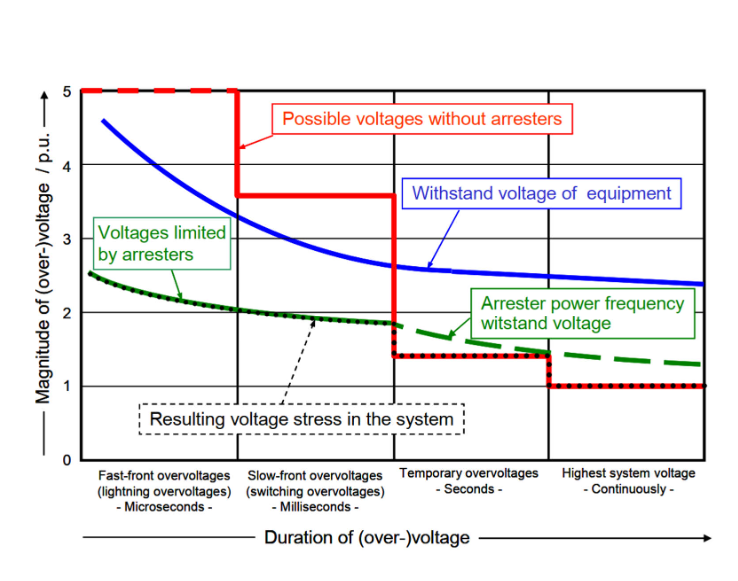
Surge Arrestor:
The Surge arresters are connected across an equipment and act like an open circuit (hight resistance) during normal operating condition and provide a low-resistance path to limit the overvoltage during the transient conditions.
Point on Wave (POW) Controllers:
Unlike the surge arresters, the point on wave controllers used to open and close the circuit breakers at the pre-determined point on the voltage wave in order to reduce the switching transients.
Data required for insulation coordination study:
The following basic information’s are required for any type of insulation coordination study are as follows:
- Goal of the Study
- Single line diagram shows the connection.
- Breaker details
- Probability and intensity of the Lightning Flash
- Ground Flash Density
- Overhead line / Cable configuration
- Failure rate of the Overhead line shield if known
- Types of Insulation used in the equipment.
- Basic Insulation Level (BIL), Basic Switching Impulse Insulation Level (BSL) and critical flashover voltage (CFO)
- Mean Time Between Surges (MTBS) and Mean Time Before Failure (MTBF)
- Geographical and atmospheric data of the location.
- Specification of underground cables, Overhead lines.
- Calculating Backflash Rate (BFR)
- Gantry and Tower Configurations
- Equipment ratings and its inductive and capacitance
- Surge Arrester parameters such as VI Curve and rating.
Analysis used in insulation coordination:
Deterministic analysis:
The Deterministic analysis consists of equating minimum strength to the maximum stress. For insulation of the equipment that cannot self-heal following a dielectric breakdown, such as transformers or cables, this analysis is used. This equipment have specific withstand voltage which is called Basic Insulation Level (BIL), that is determined by type test.
Probabilistic analysis:
Probabilistic analysis consists of selecting the insulation level and clearances based on specific reliability criteria. Probabilistic analysis mostly carried out with the help of computer based software due to the nature of its complexity.
Software’s used to do insulation coordination study:
The following software are commonly used to conduct the insulation coordination studies:
- PSCAD / EMTDC (Power Systems Computer Aided Design)
- EMTP-RV ( Electromagnetic Transients Program)
- ATP-EMTP ( Alternative Transients Program )
Power Projects have the PSCAD software to do the various insulation coordination studies. For enquires please contact Power Projects through the below link.
https://powerprojectsindia.com/insulation-coordination-studies/



No comment