Arc Flash Study & Assessments
Arc flash study is very crucial in power systems. An arc flash is a phenomenon where a flash-over of electric current leaves its intended path and travels through the air from one conductor to another, or to ground. The results are often violent and when a human is in close proximity to the arc flash, serious injury and even death can occur. Arc flash can be caused by many things including: Dust, Dropping tools, Accidental touching, Condensation, Material failure, Corrosion, Faulty Installation.
The factors to determine the severity of an arc flash injury are Proximity of the worker to the hazard, Temperature, fault current and Time for circuit to break. The main objective of an arc flash study is to identify and analyze high risk arc flash areas in your electrical power system with greater flexibility by simulating and evaluating various mitigation methods in arc flash study.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has developed specific approach boundaries designed to protect employees while working on or near energized equipment. These boundaries are
- Flash Protection Boundary (outer boundary)
- Limited Approach
- Restricted Approach
- Prohibited Approach (inner boundary)
Latest Projects
Check out our latest power system study projects around the world
The Purpose of Arc Flash Hazard Study and Analysis
- To specify the hazard / risk category
- To recommend suitable PPE for the safety of workers.
- To generate suitable danger and warning labels.
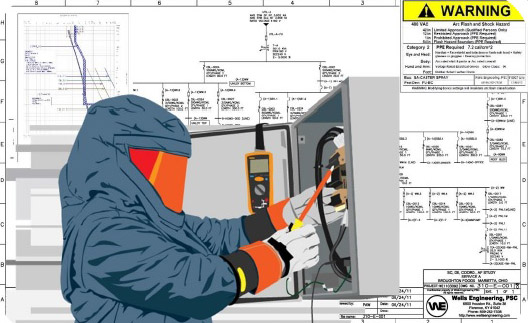

STEPS TO CONDUCT AN ARC FLASH STUDY
An arc flash study is a comprehensive analysis of a facility’s electrical system to identify potential hazards associated with arc flashes, and to recommend safety measures that can be taken to mitigate these hazards. The following steps are typically involved in performing an arc flash study:
1. Gathering data: The first step is to gather information about the electrical system, such as single-line diagrams, equipment ratings, and fault current and protection settings. This information is used to create a detailed model of the electrical system.
2. Modeling the electrical system: Using Power System Simulation software (ETAP), the electrical system is modeled in detail, including all electrical components, protective devices, and cables. This model is used to calculate the magnitude of fault currents that can flow through the system in various fault scenarios.
3. Identifying potential arc flash hazards: Based on the fault current calculations, potential arc flash hazards are identified, including the arc flash boundary, incident energy, and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements.
4. Recommending mitigation measures: Based on the hazard analysis, the study team may recommend various mitigation measures, such as protective relaying and coordination, equipment upgrades, arc-resistant switchgear, and labeling requirements. The goal is to reduce the likelihood of an arc flash event and minimize the severity of the event if one does occur.
5. Documenting the results: The study team typically prepares a comprehensive report documenting the results of the arc flash study, including recommendations for mitigation measures, arc flash hazard labels, and PPE requirements.
6. Ongoing maintenance: Once the study is complete, it is important to maintain the electrical system and update the study as changes are made to the system, such as adding or removing equipment, or changing protective device settings. This ensures that the study remains accurate and up-to-date.
It’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest industry standards and guidelines, IEEE 1584-2018, which provides updated methods for calculating arc flash hazards in AC and DC systems.
Prestigious Customers




















